
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)
What Is Basal Cell Carcinoma?
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC) is the most common type of skin cancer, making up around 80% of non-melanoma skin cancers. It arises from the basal cells in the skin’s outer layer (epidermis), typically due to long-term sun exposure.
BCC grows slowly and rarely spreads to other parts of the body, but it can cause significant damage to surrounding tissue if not treated early.
What Does BCC Look Like?
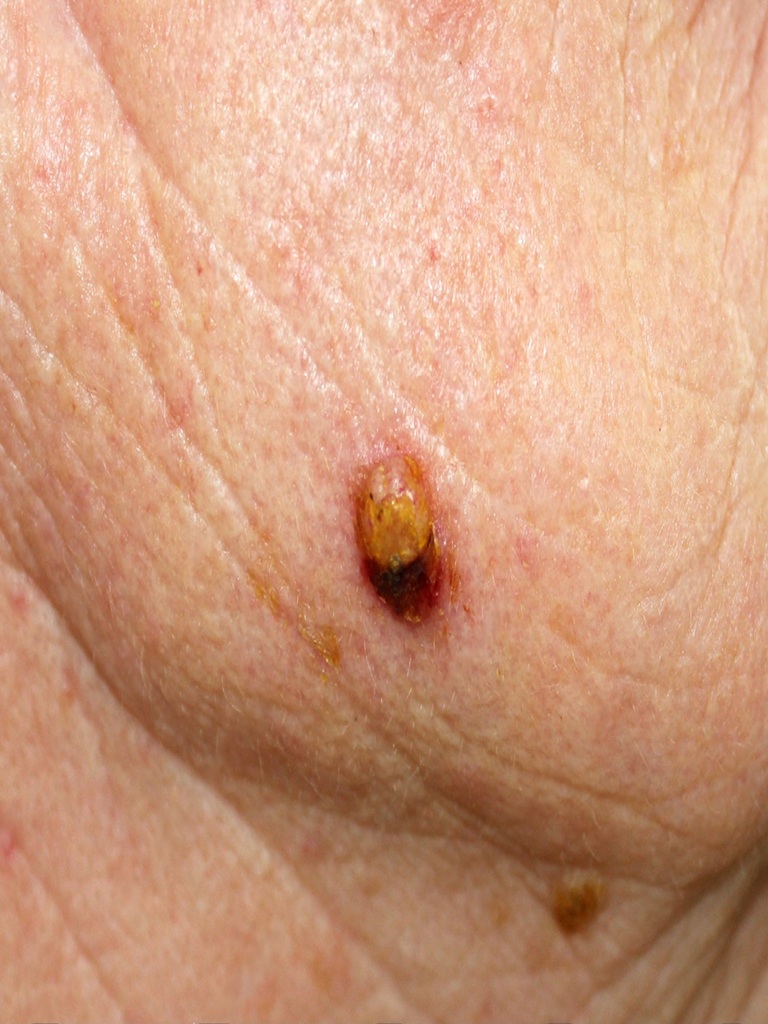
BCC can appear in many forms. Common signs include:- A pearly or waxy bump with visible blood vessels
- A flat, scaly patch that may look like eczema
- A sore that bleeds, crusts, or won’t heal
- A pink growth with a raised edge
- A scar-like area that’s firm and pale
How Is BCC Treated?
At Bollin Clinic we offer effective, evidence-based treatments tailored to your specific case.-
1. Diagnosis
- Comprehensive skin examination
- Dermatscope to assess the lesion in detail
- Biopsy (if needed) to confirm the diagnosis 2. Treatment Options
- Surgical Excision – The most common and effective treatment. We remove the cancer and some surrounding tissue.
- Curettage & Cautery – The lesion is scraped away, and the area is sealed with heat.
- Cryotherapy – Freezing with liquid nitrogen (suitable for small, superficial BCCs).
- Topical Creams – Used for specific superficial cases.
Treatment depends on the type, size, depth, and location of the BCC:
Most procedures are done under local anesthesia with minimal downtime.
Who Is at Risk for BCC?
- Have had significant sun or UV exposure
- Have fair skin, light eyes, or blonde/red hair
- Are over age 50
- Have a history of sunburns
- Use tanning beds
- Have had previous skin cancers
You may be at higher risk if you:

Basal Cell Cancer Treatment
Frequently asked questions
Is BCC dangerous?
BCC is rarely life-threatening, but it can be locally destructive. If left untreated, it can damage skin, muscle, and even bone in some areas (especially on the face).
Does it spread to other organs?
Unlike melanoma, BCC very rarely spreads (metastasizes). However, it can grow deep and become disfiguring if not treated.
Is treatment painful?
No. All treatments are done with local anesthesia. Afterward, there may be mild discomfort, which is easily managed.
Will I have a scar?
Most BCC treatments result in a small scar. We use cosmetically sensitive techniques, especially for facial lesions.
Will it come back?
Recurrence is possible, especially if the lesion is not completely removed or if you’re prone to skin cancers. Regular skin checks are important.
